What is ENERGY STAR Certification?
ENERGY STAR for New Construction is a certification program developed by the EPA and built on the HERS rating process. Offering more than just efficient appliances, ENERGY STAR-certified homes integrate energy efficiency from the ground up to deliver homes that perform at least 20% more energy efficient than homes built to code. ENERGY STAR homes boast better comfort, lower bills, and fewer callbacks – and now with a $2500 builder tax credit tied to ENERGY STAR certification, why WOULDN’T you certify your projects? Most builders assume major spec changes will be needed but in fact, you may be closer to building an ENERGY STAR-certified home than you think.
Pro-Tip
Get your plans evaluated BEFORE you’ve started construction! Many program requirements are hard to meet once framing has started, and homes that go into sheetrock without the required insulation inspection by a Home Energy Rater cannot be certified.
ENERGY STAR Program Requirements
The ENERGY STAR program can be broken into two main sets of requirements – prescriptive and performance. Both prescriptive and performance measures must be met to achieve the ENERGY STAR certification.
🌟Are you an ENERGY STAR?
Many builders are already utilizing ENERGY STAR building strategies. If the below sounds like you, you are well on your way to being an ENERGY STAR!
- HERS rating in the low 60s
- Sealed crawlspace / insulated slab
- Advanced framings such as California corners and ladder blocking
- Fresh air ventilation system
- Kitchen range exhausts to outside
- No vent-free fireplaces in conditioned space
Contact us for a project review to see how close you may be to achieving ENERGY STAR Certification
The good news is that a variety of materials and strategies can be used to achieve compliance, providing builders the flexibility to certify projects of any style and price range. While the requirements are quite detailed, we have found the best way to evaluate your projects is to meet with an ENERGY STAR Rater before you start construction to identify the best, most affordable strategies for your product type. To get the conversation started, we’ve listed a few of the more challenging ENERGY STAR items below for your consideration.
Most Common Upgrade Requirements for ENERGY STAR Certification
Building Envelope
- Windows with U values of .30 or lower and SHGC of .25 or lower
- Insulation installed with no gaps or compression and with fully aligned air barriers. Poorly installed insulation is the number 1 cause of comfort issues – I’m looking at you bonus room knee walls and garage ceiling insulation!
- Advanced Framing with insulated headers OR continuous insulation on exterior walls to reduce thermal bridging
- Drywall sealed to top plate at all unconditioned attic/wall interfaces using sill seal or a foam gasket material
- Recessed lights adjacent to unconditioned space must be ICAT (insulation contact airtight) labeled and gasketed
Download our building science guide for a refresher on best practices & high-performance strategies →
HVAC
- HVAC contractor must be an ENERGY STAR certified contractor (alternative compliance path available for projects with non-qualifying contractors)
- Bedrooms must have transfer grills, jumper ducts, or true returns to achieve pressure balancing
- Fresh air ventilation installed in compliance with ASHRAE 62.2
- MERV 6 filters for ducted systems
- No unvented combustion appliances (including fireplaces) in conditioned space
- Kitchen range exhausts to the outdoors
- Bath fans rated 80 cfm or higher in full baths
Performance
- HERS score in the mid-50s to low 60s
- Duct leakage no more than 4% outside conditioned space and no more than 8% total
What is the DOE Zero Energy Ready Home Program?
Developed by the Department of Energy, the Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH) Program is designed to deliver “a high-performance home which is so energy efficient that a renewable energy system can offset all or most of its annual energy consumption.”
The ZERH Program builds upon the existing infrastructure of the HERS Rating System and requires the EPA’s ENERGY STAR for Homes Program and Indoor Air Plus Program as prerequisites. Typically 40%-50% more energy efficient than an average new home, the ZERH Program also adds requirements for:
- Increased energy efficiency
- Indoor air quality
- Water efficiency
- Renewable energy-ready design

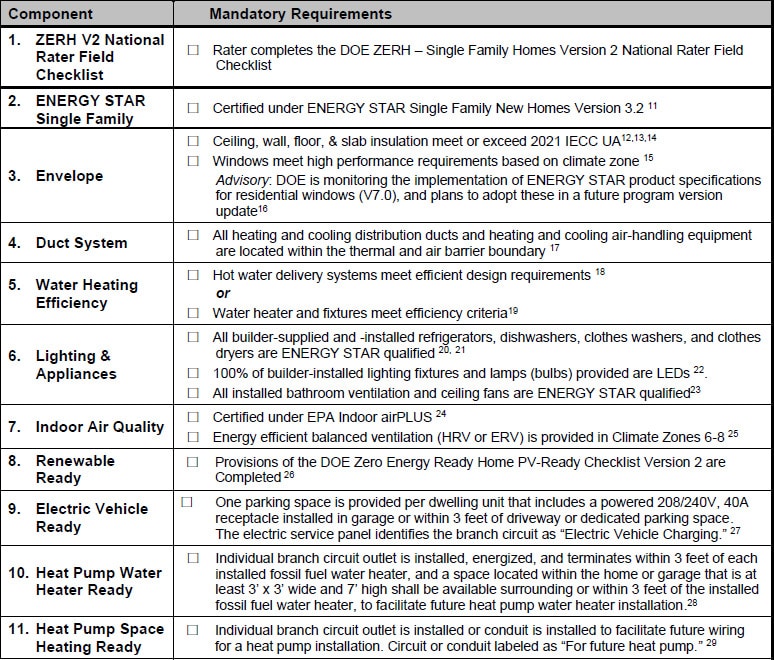
DOE ZERH Program Mandatory Requirements
The mandatory requirements of the ZERH Program are summarized in the table below. Let’s dive a little deeper into a few of them!
Envelope Upgrades to 2021 IECC Levels
This means the baseline for ZERH are the window and insulation requirements of the 2021 IECC which is more stringent than the current NC Residential code (see table below). But don’t fret if you are not installing to all of the values below – we can perform trade-off calculations to help you choose the specs that make the most sense for your products and still be in compliance.
2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) Table R402.1.3
| Climate Zone | Fenestration U-Factor | Skylight U-Factor | Glazed Fenestration SHGC | Ceiling R-Value | Wood Frame Wall R-Value | Mass Wall R-Value | Floor R-Value | Basement Wall R-Value | Slab R-Value & Depth | Crawl Space Wall R-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 49 | 20 or 13&5ci or 0&15ci | 8/13 | 19 | 5ci or 13 | 10ci, 2 ft. | 5ci or 13 |
| 4 (except Marine) | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 60 | 30 or 20&5ci or 13&10ci or 0&20ci | 8/13 | 19 | 10ci or 13 | 10ci, 4 ft. | 10ci or 13 |
| 5 (and Marine 4) | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 60 | 30 or 20&5ci or 13&10ci or 0&20ci | 13/17 | 30 | 15ci or 19 or 13&5ci | 10ci, 4 ft. | 15ci or 19 or 13&5ci |
HVAC and Duct Systems in Conditioned Space
HVAC equipment AND ductwork is required to be within the home’s thermal and air barrier boundary. Areas that are considered “conditioned space” under this definition include sealed crawl spaces, unvented attics insulated at the roof deck, and insulated basements. Ductwork such as jumper ducts that are not connected to the HVAC unit may be located in attics IF all joints are fully air-sealed and the duct is fully buried under the attic insulation.
Hot Water Delivery System Design Limits Length of Hot Water Pipe Runs
This one takes planning and is best done during the design phase of your projects. In our experience, no one currently plans the location of their water heater based on the pipe distance to the furthest fixture — and as a result, we waste a lot of energy and water waiting for hot water! To meet this requirement, you will need to limit the distance between your water heater and your furthest hot water fixture. The EPA Watersense Guide for Efficient Hot Water Delivery System has great information to help you design a compliant system.
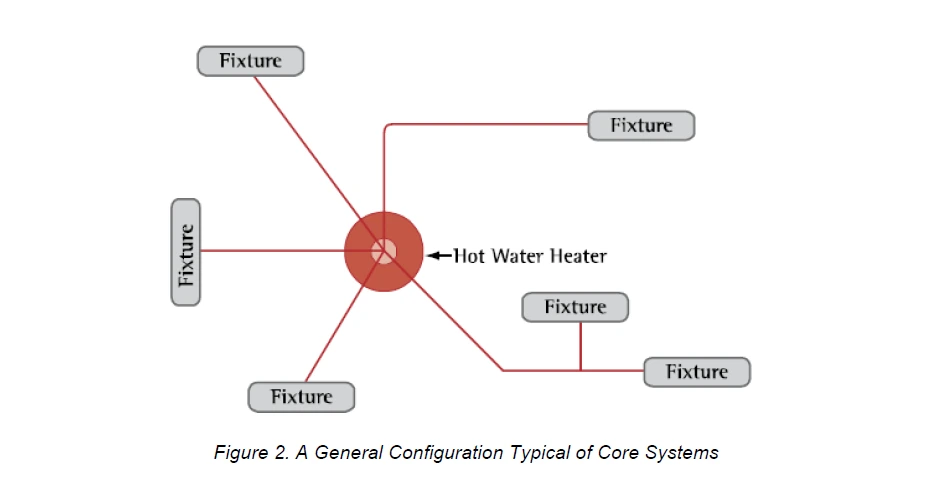
Your options for compliance are:
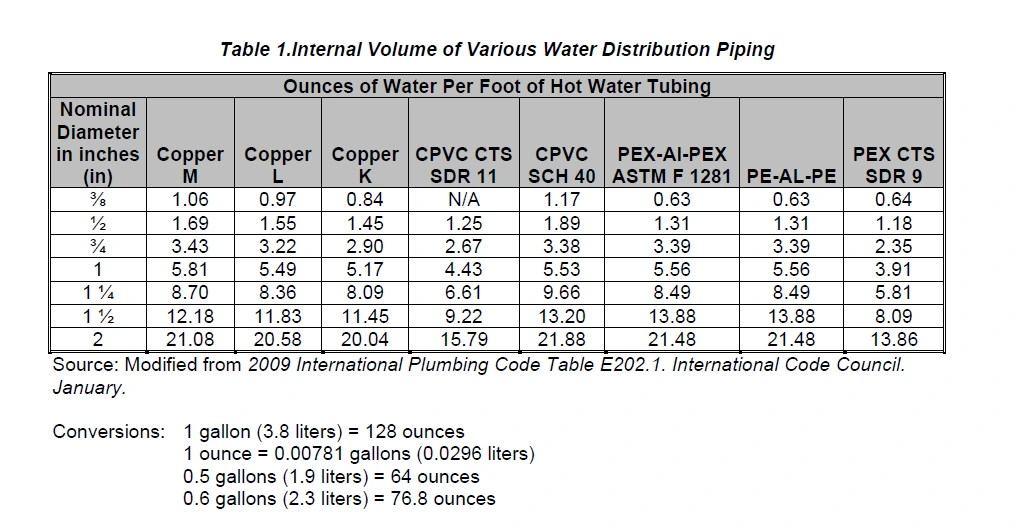
- The hot water distribution system shall store no more than 0.5 gallons (64 ounces) of water in any piping/manifold between the hot water heater and the furthest hot water fixture. For ¾” PEX that is about 18 feet (see the handy conversion chart below).
OR if you need a little more pipe run
- ALL fixtures and water heaters meet the following criteria, and the hot water distribution system is allowed to hold up to 1.8 gallons (230 ounces) from the water heater to the furthest fixture.
- Gas water heaters, if present, shall have an Energy Factor ≥ 0.90 or a Uniform Energy Factor ≥ 0.87
- Electric water heaters, if present, shall have an Energy Factor ≥ 2.2 or a Uniform Energy Factor ≥ 2.2 (typically this means a hybrid heat pump water heater)
- ALL shower heads and bathroom sink faucets shall be WaterSense labeled.
- The hot water distribution system shall store no more than 1.2 gallons (153.6 ounces) between the hot water source and the furthest fixture (For ¾” PEX which is about 45 feet).
**Note that under both scenarios, if recirculation systems are used they MUST be based on an occupant-controlled switch or an occupancy sensor.
Indoor airPLUS
Indoor airPLUS is a labeling program that has its own set of requirements summarized in a verification checklist. Requirements include, but are not limited to, moisture control practices, containment control, managing combustion pollutants, and limited emissions and VOCs from materials. Southern Energy Management is able to provide the verification and certification services needed to get Indoor airPLUS certified.

EV and Heat Pump Water Heater Ready
These requirements are focused on ensuring homes can accommodate electric vehicles and heat pump water heaters in the future. Design specifics are detailed in the mandatory requirements chart, but the two main criteria to be “ready” are:
- Dedicated circuits for a future EV charger and a future heat pump water heater (don’t forget to make sure your electric panel is sized appropriately)
- Dedicated space for a future EV charger and a future heat pump water heater

Renewable Ready
The requirement your partnership with Southern Energy Management has been waiting for – we are here to help you SHINE! And for those of you already part of our Zero Energy Blueprint Program, this requirement is met! If you are new to the concept of including solar as an option for your home, don’t worry, being “PV Ready” is much easier than you think. To meet this requirement, Southern Energy Management will provide you with a free custom solar quote for your plan and specifications on where to include the required conduit for future PV wiring. AND if your site has significant natural shading or your design does not have between 100 – 400 square feet of free roof area within 45 degrees of south, you are exempt from this requirement.



Certification Process and Next Steps
- Submit your plans and specs to Southern Energy Management (SEM) for energy modeling before construction starts to determine materials and equipment needed to achieve the energy efficiency target
- Include all mandatory requirements in design
- Schedule your insulation and final inspections with SEM – we will Inspect and verify program requirements throughout the construction process
- Pass your inspections and receive program certification
- Get that tax credit!
We’re here to help! Schedule a meeting today to get started →















